Statistics
- Online212
- Today47,564
- This month1,401,979
- Total42,668,954
Diagnosis of spastic cerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy is a term that refers to a group of medical conditions due to CNS damage that do not progress over time, caused by causes before birth, during and after birth until less than 5 years of age, causing multiple conditions. disabilities in movement, mind, senses and behavior... leaving heavy consequences not only for the children themselves and their families but also for their economic and social development.
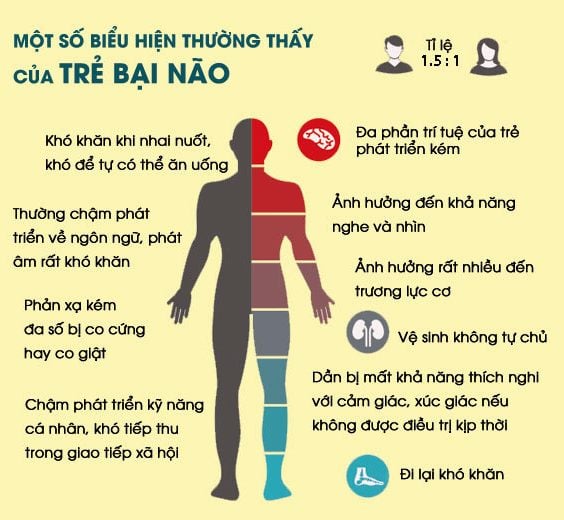
Based on clinical symptoms, cerebral palsy is classified into the following diseases:
Spasticity; Can dance around ; Ataxia (loss of coordination); Flatulence (hypotonicity); Mixed body (usually a combination of spasticity and schizophrenia).
Criteria for the diagnosis of spastic cerebral palsy include:
Increased muscle tone in the affected limbs occurs when the child tries to move, especially when balancing, this symptom is very evident in children severe spasticity. In children with severe spastic cerebral palsy, the muscles are in a state of co-contraction, that is, all the muscles of the limbs and trunk are spastic; Decreased mobility in individual joints; Signs of damage to the pyramidal system; Increased tendon reflexes in limbs damaged by increased muscle tone; There are primitive reflexes in infants over six months of age and pathological reflexes. Normal infant reflexes usually disappear before the baby is 6-12 months old. Doctors can check your baby's medical history and try to rule out other disorders that may cause similar symptoms. Sensory dysregulation may be present; Possible paralysis of the cranial nerves; Other signs: foot tremors, contractures in joints, scoliosis, epilepsy....; Mental retardation of different degrees.
2.1. Indications Brain tumors that are invasive or adjacent to axonal bundles; Cases needing diagnosis of spastic cerebral palsy with suspicion of axonal damage; Multifocal sclerosis, white matter lesions in infarction, bleeding,...; Cerebral vascular malformations, need to find the relationship between the malformation and the axon bundle; Congenital malformations: ectopic gray matter, cleft encephalopathy...; Epilepsy. 2.2. Contraindications Magnetic resonance imaging is not performed in the following cases:
General contraindications; Patients carrying a pacemaker are not allowed to diagnose cerebral palsy by magnetic resonance imaging; A note during magnetic resonance imaging is that the patient needs to remove jewelry and magnetic metal tools on the body. Therefore, before taking magnetic resonance imaging, the patient needs to report to the doctor and technician about the means of support on the body to have a specific solution for each case.
2.3. Advantages Force-diffusion imaging is an imaging technique developed from simple diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. This technique allows determining the direction as well as the magnitude of the diffusion; The ability to detect the paths of nerve fiber bundles in the brain using force-diffusion imaging is known as bunion. Bundle imaging allows the creation of two- or three-dimensional images of the brain's nerve fiber system; In brain tumors, magnetic resonance imaging technique allows to determine the invasion or compression of nerve fiber bundles, associated brain tumor and nerve fibers, very important information in the diagnosis of spastic cerebral palsy; Diffuse magnetic resonance imaging provides additional important information about many pathological processes in the skull that conventional magnetic resonance cannot or is difficult to evaluate such as in tumorigenesis, inflammation, white matter disorders, etc.
Spasticity; Can dance around ; Ataxia (loss of coordination); Flatulence (hypotonicity); Mixed body (usually a combination of spasticity and schizophrenia).
1. Diagnostic criteria for spastic cerebral palsy
When a patient is diagnosed with spastic cerebral palsy, in addition to asking the patient, taking the history, and doing a physical exam to find out and determine the cause of the cerebral palsy, the doctor will probably perform a number of tests. necessary functional tests such as: magnetic resonance imaging, electroencephalogram, brain ultrasound through the fontanelle, performing psychological assessments... to find out the cause of the disease and assess the patient's cognitive ability.Criteria for the diagnosis of spastic cerebral palsy include:
Increased muscle tone in the affected limbs occurs when the child tries to move, especially when balancing, this symptom is very evident in children severe spasticity. In children with severe spastic cerebral palsy, the muscles are in a state of co-contraction, that is, all the muscles of the limbs and trunk are spastic; Decreased mobility in individual joints; Signs of damage to the pyramidal system; Increased tendon reflexes in limbs damaged by increased muscle tone; There are primitive reflexes in infants over six months of age and pathological reflexes. Normal infant reflexes usually disappear before the baby is 6-12 months old. Doctors can check your baby's medical history and try to rule out other disorders that may cause similar symptoms. Sensory dysregulation may be present; Possible paralysis of the cranial nerves; Other signs: foot tremors, contractures in joints, scoliosis, epilepsy....; Mental retardation of different degrees.
2. Diagnosis of spastic cerebral palsy by magnetic resonance imaging
Conventional magnetic resonance imaging: Magnetic resonance imaging of nerve fibers (tractography) or Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) is an advanced imaging technique, applied in the diagnosis of diseases. Neuropsychology to diagnose the cause of cerebral palsy when axonal damage is suspected or it is necessary to find a relationship between the lesion and axon to avoid axonal damage when interfering with the lesion.2.1. Indications Brain tumors that are invasive or adjacent to axonal bundles; Cases needing diagnosis of spastic cerebral palsy with suspicion of axonal damage; Multifocal sclerosis, white matter lesions in infarction, bleeding,...; Cerebral vascular malformations, need to find the relationship between the malformation and the axon bundle; Congenital malformations: ectopic gray matter, cleft encephalopathy...; Epilepsy. 2.2. Contraindications Magnetic resonance imaging is not performed in the following cases:
General contraindications; Patients carrying a pacemaker are not allowed to diagnose cerebral palsy by magnetic resonance imaging; A note during magnetic resonance imaging is that the patient needs to remove jewelry and magnetic metal tools on the body. Therefore, before taking magnetic resonance imaging, the patient needs to report to the doctor and technician about the means of support on the body to have a specific solution for each case.
2.3. Advantages Force-diffusion imaging is an imaging technique developed from simple diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. This technique allows determining the direction as well as the magnitude of the diffusion; The ability to detect the paths of nerve fiber bundles in the brain using force-diffusion imaging is known as bunion. Bundle imaging allows the creation of two- or three-dimensional images of the brain's nerve fiber system; In brain tumors, magnetic resonance imaging technique allows to determine the invasion or compression of nerve fiber bundles, associated brain tumor and nerve fibers, very important information in the diagnosis of spastic cerebral palsy; Diffuse magnetic resonance imaging provides additional important information about many pathological processes in the skull that conventional magnetic resonance cannot or is difficult to evaluate such as in tumorigenesis, inflammation, white matter disorders, etc.
Note: The above article reprinted at the website or other media sources not specify the source http://nukeviet.vn is copyright infringement
Reader Comments
You need to log in as Member to be able to comment














